Charting the Future of Care: Understanding the Rapid Rise of FDA-Approved AI Devices
Rapid advances in artificial intelligence (AI) have reshaped the landscape of medical innovation, culminating in an unprecedented surge of FDA-approved AI-enabled medical devices over the past decade. According to data compiled by Stanford Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI) in collaboration with the FDA, the tally of new AI-enabled medical devices approved each year has climbed steeply from just a handful before 2016 to well over two hundred in 2023. This graphic paints a vivid portrait of that growth: a near-flat line through the early 2000s, a gentle uptick around 2014, and then an almost exponential rise from 2018 onward. Understanding the forces behind this rapid ascent—policy shifts, research funding, technological maturation, and clinical adoption—offers crucial context for anyone engaged in Healthcare Discovery AI. In this article, we explore how government research budgets have fueled the AI pipeline, examine regulatory initiatives that have accelerated device review, highlight notable early adopters of AI in healthcare, and ultimately position Healthcare Discovery AI to harness these trends in service of clinicians, researchers, and patients.
Between 1995 and 2015, the annual count of FDA-approved AI-enabled medical devices hovered near single digits. Technology at that time was often limited by immature machine learning algorithms, underpowered compute platforms, and sparse regulatory precedents for software-based medical tools. A small trickle of image segmentation algorithms for radiology emerged, but those early approvals signified more promise than scale. It was only after 2016—when several factors converged—that the slope of device approvals began to steepen. By 2017, eighteen new AI-enabled medical devices had gained FDA clearance; in 2018, twenty-six; and in 2019, sixty-four. That upward trajectory accelerated dramatically in subsequent years, reaching eighty approvals in 2020, one hundred fourteen in 2021, one hundred twenty-nine in 2022, and one hundred sixty in 2023. The data point that truly stands out is the jump to two hundred twenty-three approvals in 2023, underscoring that AI in healthcare is far beyond an early adopter phase and well into mainstream validation.
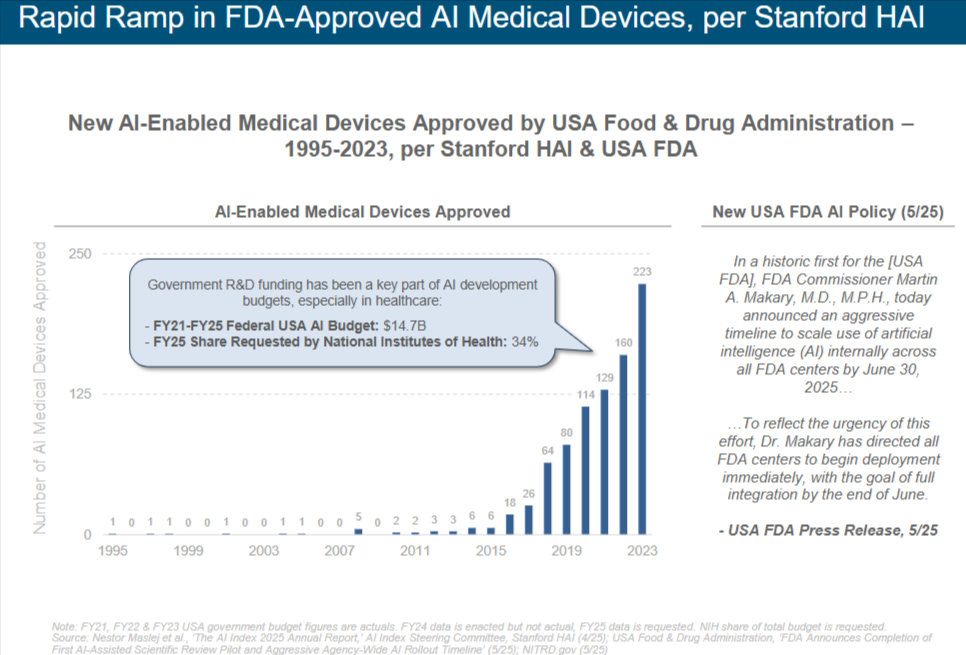
Government R&D funding has proven to be a cornerstone of AI development, with the healthcare sector among the largest beneficiaries. Between fiscal years 2021 and 2025, the United States federal government allocated approximately fourteen point seven billion dollars toward AI research. This infusion of capital powered breakthroughs in core machine learning research, fostered interdisciplinary collaborations between computer scientists and clinicians, and supported pilot programs that demonstrated clinical value. Within that broader AI budget, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) requested a significantly higher share for AI research in 2025—roughly thirty-four percent of its total budget—reflecting a clear prioritization of AI tools to address unmet medical needs. Grants targeting AI for radiology, pathology, genomics, and population health have seeded dozens of academic labs and startup ventures. Many of those projects matured into products that underwent FDA’s Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) pathway, ultimately contributing to the growing number of approved devices seen in the chart.
Beyond raw funding, federal agencies have also sought to streamline regulatory pathways for AI-enabled devices. Historically, the FDA had limited experience with machine learning algorithms that continuously evolve based on new data. Traditional device approvals tended to rely on static performance benchmarks, leaving developers to struggle with how to validate algorithms that might update in the field. Recognizing this gap, the FDA introduced a proposed regulatory framework in late 2019 that described a “Predetermined Change Control Plan” to guide developers on how AI/ML-enabled SaMD could adapt post-approval. By outlining good machine learning practices, safety metrics, and retraining protocols, the FDA signaled to innovators that adaptive AI workflows could be accommodated without re-submitting an entire application. This regulatory shift paved the way for startups and established medical device companies alike to invest more confidently in AI research, knowing that the path from prototype to clearance would not be obstructed by opaque requirements.
In May 2025, the FDA took another momentous step by announcing an agency-wide AI policy that mandates all FDA centers to scale use of AI internally by June 30, 2025. Commissioner Martin A. Makary, M.D., M.P.H., emphasized that this aggressive timeline reflects the urgency of integrating artificial intelligence into regulatory review, inspectional processes, and public health surveillance. By directing immediate deployment of AI tools across centers, the FDA aims to harness machine learning for tasks such as adverse-event signal detection, automated review of premarket submissions, and predictive analytics for inspection scheduling. This internal adoption creates a virtuous cycle: as the FDA gains firsthand experience with AI’s capabilities and limitations, its guidance documents and review expectations will become more precise. Device developers can then align their submissions more closely with regulators’ evolving criteria, thereby reducing review times and enabling faster market access.
Clinical adoption has followed regulatory momentum. Hospitals, imaging centers, and outpatient clinics are now increasingly embedding AI-enabled decision support tools within radiology workstations and electronic health record (EHR) systems. Leading academic medical centers were among the first to pilot AI algorithms for tasks such as detecting intracranial hemorrhage on CT scans, identifying diabetic retinopathy in fundus photographs, and triaging pulmonary embolism findings on CT angiograms. As real-world evidence from these pilot deployments accumulated, payers and hospital administrators recognized the potential for AI to improve diagnostic accuracy, reduce time to treatment, and lower costs associated with missed or delayed diagnoses. Reimbursement policies began to reflect this recognition: in 2021, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) rolled out new billing codes for AI-assisted medical imaging interpretation, signaling that such tools would be compensated, not viewed as experiments. With reimbursement secured, deployment expanded beyond academic centers to community hospitals and private practices, widening the market for AI-enabled medical devices and encouraging new entrants.
The timeline from initial FDA submission to market may still span several years, but once a device gains clearance, adoption can be remarkably rapid. Consider an AI algorithm for mammography interpretation that achieved de novo clearance in late 2019. Within eighteen months, it was deployed across hundreds of imaging centers nationwide. Similarly, AI systems for automated bone age assessment—once novel pilot products—are now common fixtures in pediatric radiology suites. Ophthalmology has seen a parallel trajectory: after the first autonomous AI system for diabetic retinopathy received FDA approval in 2018, eager ophthalmic practices established protocols to screen high-risk diabetic patients at primary care offices, referring positive cases to specialists in a fraction of the time conventional workflows would allow. These success stories underscore how once a critical mass of peer-reviewed clinical validation emerges, the momentum behind AI device adoption accelerates markedly.
Naturally, the remarkable growth in device approvals raises questions about quality, bias, and equity. AI models trained on homogeneous patient populations risk underperforming when applied to demographic groups underrepresented in training data. Addressing these concerns has become an integral part of the approval process: the latest FDA guidance explicitly requests developers to demonstrate model performance across diverse cohorts, to mitigate disparities in outcomes. Post-market surveillance plans for AI devices frequently include monitoring real-world performance stratified by age, sex, race, and socioeconomic status. Moreover, some device developers have opted for federated learning architectures, enabling models to learn from decentralized datasets housed across partner institutions without transferring raw patient data. These approaches promise to reduce bias by exposing DL algorithms to heterogeneous clinical environments, further solidifying the foundation upon which the FDA approves new devices.
Aside from improving diagnostics and workflows, AI-enabled devices are also beginning to redefine therapeutic interventions. Robotic surgical systems with integrated AI modules can now autonomously identify anatomical landmarks in real time, guiding surgeons with augmented reality overlays. Early adopters have reported reductions in operating times and improved suturing precision in procedures such as prostatectomy and partial nephrectomy. At the same time, AI-driven infusion pumps dynamically adjust drug delivery based on continuous vital sign monitoring, optimizing fluid balance in critically ill patients. Though these therapeutic devices currently represent a smaller fraction of FDA approvals compared to diagnostic systems, their growth trajectory is similarly steep. In 2023 alone, several novel AI-embedded therapeutic devices received expedited review, reflecting regulation that is catching up with innovation.
For Healthcare Discovery AI, these trends signal both opportunity and responsibility. As a platform designed to catalog and analyze exponential innovations in healthcare research, Healthcare Discovery AI must capture not only published manuscripts and clinical trial records but also the evolving landscape of FDA clearances for AI-driven devices. Leveraging databases such as the FDA’s Medical Device Database, Healthcare Discovery AI can continuously scrape premarket and de novo clearance announcements, indexing device names, intended use cases, performance metrics, and submission paths. By integrating that with machine-readable clinical trial registries and scientific publications, the platform can deliver real-time intelligence to healthcare executives, academic investigators, and venture capitalists seeking to understand where AI is most rapidly translating into clinical practice.
Pragmatically, Healthcare Discovery AI can provide curated insights on how FDA review pathways for AI devices have changed over time, highlighting emerging regulatory frameworks such as the Total Product Lifecycle (TPLC) paradigm for adaptive AI/ML technologies. Users might, for example, query how many devices in the oncology space received 510(k) clearance for image analysis between 2020 and 2022, compare their reported sensitivity and specificity, and cross-reference linked peer-reviewed studies demonstrating impact on clinical decision-making. This kind of longitudinal analysis would be invaluable for product planners at device firms deciding whether to invest in a new AI algorithm or to form partnerships with academic labs. By surfacing trends—such as shifts from rule-based expert systems to deep learning neural networks in specific specialties—Healthcare Discovery AI can help stakeholders identify “white space” where unmet clinical needs remain ripe for disruption.
Beyond sheer device count, Healthcare Discovery AI can spotlight notable first-in-kind approvals that presage broader technological shifts. For instance, the first FDA approval of an autonomous diagnostic system for diabetic retinopathy in 2018 marked a new era of AI-driven screening that did not require a specialist to interpret the output. Likewise, the 2021 clearance of the first AI device for COVID-19 pneumonia detection on chest radiographs illustrated how quickly AI could respond to emergent public health crises. Capturing these milestone events, along with granular details such as the training dataset size, selected algorithm architecture, and clinical validation endpoints, empowers users to draw parallels between prior waves of innovation and current frontier technologies.
Integration with Healthcare Discovery AI also facilitates a deeper exploration of how government funding sources correlate with subsequent device approvals. By mapping NIH grant IDs for AI-related research to eventual FDA submissions, the platform can demonstrate investment impact in a quantifiable way. Imagine a dashboard that shows total NIH funding awarded to computational pathology projects from 2016 to 2023 alongside the number of computational pathology devices approved in that window. Such visualizations shed light on the lag time between grant disbursement, technology maturation, and regulatory clearance. Investors and policy makers could use this intelligence to calibrate future funding allocations, ensuring that promising research areas receive sustained support into the translation phase.
Equally important is the role of Healthcare Discovery AI in monitoring compliance and post-market performance. As AI devices roll out widely, real-world evidence may reveal latent issues—algorithmic drift when trained models face new patient demographics, or cybersecurity risks when devices are connected to hospital networks. By ingesting adverse event reports, device recall notices, and publication errata, the platform can alert users to early warning signs. For device manufacturers, this capability transforms regulatory risk management from reactive to proactive. Identifying subtle performance degradation across disparate clinical sites can prompt timely software updates or retraining protocols, safeguarding both patient safety and regulatory trust.
Healthcare Discovery AI’s unique perspective also extends to competitive intelligence. Startups and established medical device companies alike will find value in tracking competitor pipelines—anticipating when a rival might file for breakthrough designation or analyzing clinical trial endpoints to gauge comparative performance. When the FDA awards breakthrough status to an AI-based therapeutic system for managing heart failure patients, for example, Healthcare Discovery AI users can immediately drill down into the predicate devices, review study designs, and examine pricing and reimbursement pathways. This breadth of insight helps organizations chart strategic partnerships, licensing deals, or M&A opportunities informed by the latest regulatory developments.
Looking ahead, the regulatory environment for AI devices promises continued evolution. The proposed AI/ML SaMD guidance is expected to be finalized soon, clarifying criteria for model transparency, interpretability, and ongoing learning. In parallel, the FDA’s Digital Health Center of Excellence aims to formalize expertise on evaluating data-centric algorithms, cloud-native design, and real-world performance metrics. These initiatives will likely reduce uncertainty for developers and accelerate approval cycles. Healthcare Discovery AI stands to benefit by integrating these policy shifts into its knowledge graph, enabling users to simulate “what-if” scenarios: for instance, “how many future AI radiology solutions could qualify for expedited review under the finalized SaMD guidance?” This foresight is crucial for innovators planning resource allocation and go-to-market timelines.
The rebound of government funding further supports this optimistic outlook. Federal investments in AI research remain robust, and new programs explicitly target health data interoperability, algorithmic bias mitigation, and digital therapeutics. The NIH’s Bridge2AI initiative, for example, has dedicated hundreds of millions of dollars to generating high-quality, multi-modal health data poised to train clinically robust AI models. By incorporating Bridge2AI grant data into Healthcare Discovery AI’s platform, users can trace emerging datasets that may seed the next generation of AI-enabled devices. This transparency not only accelerates collaboration between academic institutions but also reduces duplication of effort—ensuring that new devices leverage the latest and most diverse data sources.
Beyond U.S. borders, global regulatory agencies are starting to harmonize AI device oversight in ways that complement FDA practices. The European Union’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and its planned AI Act are converging with FDA expectations on data quality, risk classification, and post-market performance. Healthcare Discovery AI can illuminate these international parallels, helping U.S. device developers plan for multi-regional launches. By cross-referencing FDA approvals with CE markings, for instance, the platform can identify devices that cleared U.S. review but remain pending in Europe, offering clues about submission strategies and potential bottlenecks. For investors and strategic planners, this global vantage is indispensable in a marketplace where healthcare innovation transcends national boundaries.
While regulatory frameworks and funding pipelines are critical, the ultimate judge of AI-enabled devices is clinical impact. Early evidence suggests that AI tools can significantly enhance diagnostic workflows. A large observational study at a major academic hospital recently reported that an AI algorithm for stroke triage reduced time-to-interpret by an average of ten minutes, resulting in faster interventions and improved patient outcomes. In a multi-center trial published in 2022, an AI system for predicting acute kidney injury demonstrated a twenty percent reduction in incidence when clinicians followed algorithmic prompts for early fluid management. These real-world success stories not only validate the promise of AI but also underscore why the surge in FDA approvals matters: each new clearance represents a potential leap forward in patient care.
Healthcare Discovery AI can amplify these clinical narratives by linking device approvals to published outcomes studies, generating meta-analyses that quantify AI’s added value. Users might query the platform for head-to-head comparisons of AI algorithms for pulmonary nodule detection, reviewing sensitivity and specificity metrics across heterogeneous patient cohorts. By synthesizing evidence in a standardized format, Healthcare Discovery AI helps clinicians and hospital administrators make informed adoption decisions—identifying which AI-enabled devices offer the best return on investment in terms of improved diagnostic yield, workflow efficiency, and ultimately, patient safety.
Cumulatively, the sevenfold increase in FDA-approved AI devices from 2018 to 2023 is more than just data points on a chart; it represents a transformative shift in how healthcare systems generate, interpret, and act upon medical information. For innovators, investors, and clinicians alike, this dynamic environment demands a robust discovery platform—one that not only catalogues devices but also contextualizes their regulatory history, clinical impact, and market trajectory. Healthcare Discovery AI sits at the nexus of this imperative. By harnessing advanced data ingestion pipelines, natural language processing, and curated curation workflows, it transforms disparate FDA announcements, clinical trial registries, and academic publications into coherent, actionable intelligence.
In practical terms, a healthcare entrepreneur seeking to develop the next AI-based cardiology device can begin by exploring Healthcare Discovery AI’s device library, identifying gaps in existing approvals—perhaps noting that while AI tools for left ventricular ejection fraction estimation are abundant, few solutions have addressed right ventricular strain analysis. By reviewing regulatory clearance dates, performance benchmarks, and post-market surveillance reports, the entrepreneur gains clarity on where to differentiate and how to align prospective device filings with FDA guidance. In parallel, venture capitalists looking to invest in early-stage AI medtech can leverage Healthcare Discovery AI to screen startups that have secured NIH grants and clarified FDA submission strategies, thereby triangulating technical merit, regulatory feasibility, and market demand.
The ongoing march toward real-time monitoring and adaptive learning further elevates the need for a platform that tracks AI device evolution continuously. Future devices may incorporate federated learning across institutions, self-monitor for performance drift, or deploy explainable AI modules that satisfy both clinician trust and regulatory transparency. Healthcare Discovery AI is uniquely positioned to capture these transitions, offering a longitudinal lens that traces the journey of individual devices from research labs to patient bedside. Its analytics could reveal, for instance, that devices employing federated learning architectures achieved faster FDA approval when developers partnered with multiple academic medical centers—a lesson that can guide consortium-based development models in the years ahead.
As the FDA’s May 2025 AI policy unfolds, directing each center to embed artificial intelligence in its workflows, we can anticipate even shorter review cycles, more consistent expectations around continuous learning algorithms, and heightened emphasis on ethical AI. These regulatory advances will serve as tailwinds for device developers, while also raising the bar for transparency and post-market vigilance. For Healthcare Discovery AI users, this translates to a more abundant stream of high-fidelity data, from real-time clearance announcements to detailed policy guidance documents. By parsing these materials, the platform can generate customized alerts—whether notifying users when a new AI-based dermatology device secures FDA de novo clearance or flagging draft guidance on algorithmic transparency that may affect pending submissions.
In conclusion, the graphic showcasing the rapid ramp in FDA-approved AI-enabled medical devices is not merely a statistical artifact but a harbinger of a profound transformation in healthcare delivery. Underpinned by robust government research funding, evolving regulatory pathways, and validated clinical outcomes, AI devices have vaulted from niche pilots to widespread clinical integration in just a few years. For those building and deploying AI-driven solutions—whether in medical imaging, genomic analysis, digital therapeutics, or robotic surgery—understanding this trajectory is essential. Healthcare Discovery AI emerges as an indispensable partner in this journey: a comprehensive, dynamic platform that bridges the gap between raw regulatory data, scientific publications, and actionable clinical insights. By enabling stakeholders to track device approvals, scrutinize performance metrics, and anticipate policy shifts, this platform not only supports informed decision-making but also accelerates the translation of AI innovations into meaningful improvements in patient care. As the field of AI in medicine continues its upward trajectory, having a reliable compass to navigate its complexities will be key—and Healthcare Discovery AI stands ready to deliver precisely that guidance.